Collecting and analyzing data is vital for organizations that provide important services to community members. Accurate, relevant data allows you to report on outcomes, secure grant funding, and so much more. When used properly, data can take your nonprofit organization or public sector agency to new heights in terms of delivered outcomes, funding, growth trajectory, and most importantly, impact.
But how do you decide what data to track, how to house it efficiently, and how to turn data into more effective service delivery? The answer is data maturity. Let’s go over what data maturity is and how you can measure yours with the data maturity model.
What is data maturity?

Data maturity is a measurement of how sophisticated an organization’s data analysis and management systems are, often measured by a data maturity model.
Becoming data-mature involves creating more sophisticated data collection and analysis processes, building out data governance, and using data to drive decision-making. Highly mature nonprofits and public sector agencies treat data as the core of everything they do to make their operations more efficient and impactful.
What is a data maturity model?
A data maturity model is a system intended to help you map your data journey by providing insight into where you are in terms of data maturity and how to improve. It gives you more direction for your data maturity journey and shows you a clear path to growth.
Since every organization and agency uses a different data management process, data maturity won’t look the same for everyone. Depending on factors like geographical service area, staff size, budget, and service delivery methods, the data you collect may vary greatly. However, using a focused “data map” to chart your path to greater data sophistication can help any organization achieve long-term impact.
Why are data maturity models important?
The direction that a data maturity model provides helps your organization stay focused on moving toward data maturity and gives you concrete steps to propel you further in the process. Ultimately, using a model to become more data-mature can help your organization:
- Chart your path to better data management systems
- Get more visibility into your programs and service delivery
- Save team time by creating more efficient processes
- Streamline and improve reporting for grants
- Give your team more time to focus on service delivery
- Demonstrate impact to funders more easily and accurately, helping you get more funding in the future
- Make better decisions based on data
- Achieve more positive outcomes for clients and community members
Along with these benefits, becoming data-mature at an organizational level also helps your staff members develop their data literacy skills. When your staff can confidently track outputs and manage outcomes, they can improve their own service delivery at your agency and beyond.
The 4 stages of our data maturity model
While there are several different data maturity models that you can use, we recommend using a model that focuses on impact management. Our model is designed to improve your agency’s data maturity and your ability to report on trends and drive impact.
Let’s dive deeper into the four stages of our recommended data maturity model:
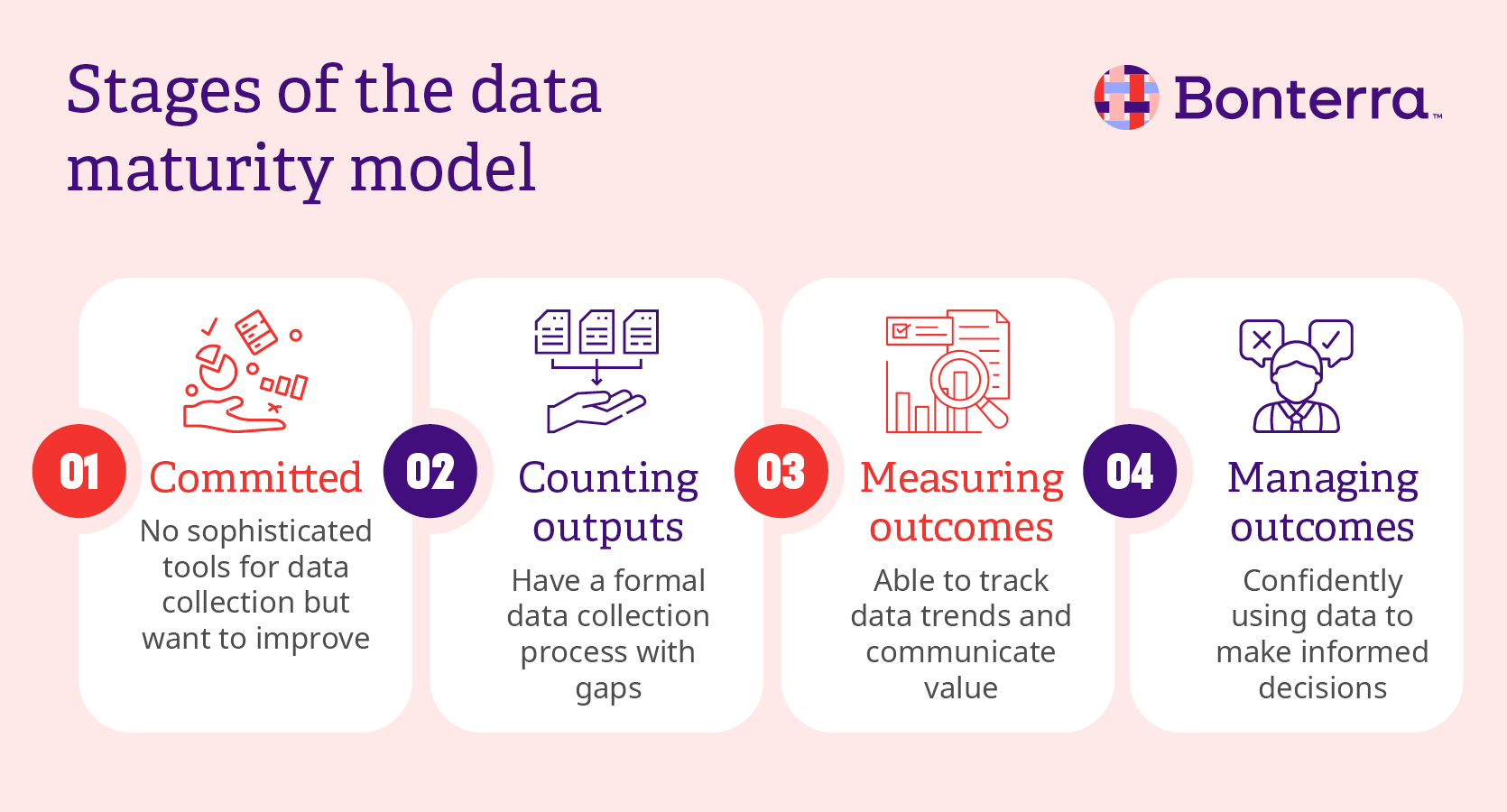
1. Committed
In this stage, you may have systems in place to collect data, but they aren’t very sophisticated.
For example, you might use paper forms to collect information about clients, and then manually input that information into a spreadsheet. You want to provide more detailed reports to your funders, but you need new tools or more staff time to do so. As a result, you’re more reactive than proactive when it comes to your data.
If your organization is in the committed stage of the data maturity model, start having conversations with leadership and stakeholders about the role of data in your organization. Research more centralized data collection systems you might use, and choose one to implement. Then, develop a comprehensive plan that will get your new data initiative off the ground and help you move to the next level of the data maturity model.
2. Counting outputs
Agencies in the counting outputs stage have a formal data collection process. While there might be gaps in the data you collect, you’ve determined what data you need to improve your service delivery and have established a system to track those data points.
At this stage, your organization tracks specific, relevant outputs of your service delivery and programs. These concrete data points help you see how your services affect clients individually. There may be gaps in your data, but you’re working on identifying and filling these gaps to increase program visibility.
You may also have funders you need to report to in the counting outputs stage. You can effectively share data about your outputs at this point, but you need to refine your system to meet funders’ expectations in the long run.
Want to dive deeper into the first two stages of our data maturity model? Download our free, in-depth guide to learn more.
3. Measuring outcomes
In the measuring outcomes stage, you’ll go beyond laying the groundwork and start to form a systematic, organized, and possibly cloud-based data collection process.
In this stage, you can see outputs at a high level and improve your service delivery because of your ability to track key metrics. You can measure and track data trends to make short-term decisions to improve your nonprofit’s performance.
To get to this stage, you need to first understand the difference between two key terms: outputs and outcomes.
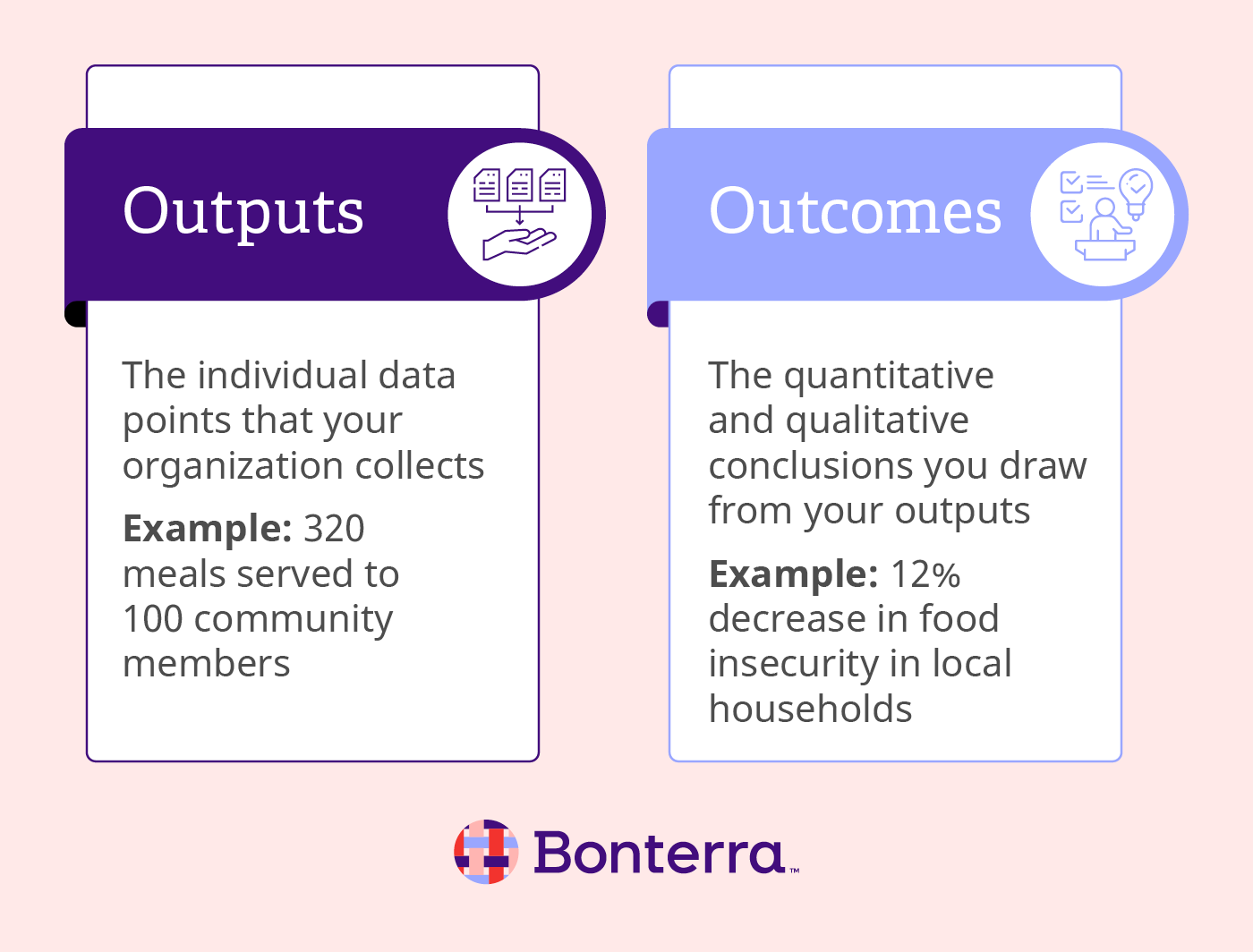
- Outputs are the individual data points that your organization collects. For example, a food bank’s output might be 320 meals served to 100 community members over the course of three months.
- Outcomes are the quantitative and qualitative conclusions you draw from your outputs. For our food bank example, measuring an outcome might be achieving a 12% decrease in food insecurity in local households.
One of the biggest turning points you’ll experience by measuring outcomes is your ability to communicate value to funders. When pulling reports and discovering trends is much easier thanks to organized data, reporting becomes more reliable and less resource-intensive. You might even see higher internal morale because you can easily see the progress and impact you’ve made.
4. Managing outcomes
In the final stage, your organization uses data optimally, and you are confident that your data is informed and accurate. You’ve mastered counting outputs and measuring outcomes, and your leadership uses collected data to make informed, real-time decisions that benefit your programs and clients.
Additionally, your organization reaches a level of high performance that allows you to continuously use resources optimally to drive impactful outcomes. It’s easy to see the effect your work has across all of your programs and different times, regions, and demographics.
Although managing outcomes is the final stage in the data maturity model, you can always improve your processes further. Practice constant vigilance to maintain data integrity and ensure that your case management system has the features to help you continue to perform at a high level.
How to identify your level of data maturity
Now that you know what the four stages look like, how do you identify which maturity level your organization is at? First, think about the following questions to get more insight into your current data practices:
- How does your organization collect data? Do you use spreadsheets, case management software, or another tool?
- Can your staff easily locate and access important data points? Is all of your data in a centralized location?
- Are your funders happy with the ways you report data? Can you use data to effectively tell your story and acquire more funding?
- Can you easily measure your programs’ and services’ impact from your data? Can you communicate that impact effectively?
- Do you use data to make decisions about your programs and services?
Your answers to these questions will help you take stock of your processes and determine which level best aligns with your current standing.
Moving through the data maturity model
As you find your place in our data maturity model and take steps to move to the next level, remember that the goal is to streamline your data management practices so you can more easily deliver and measure real impact. With the right tools and processes in place, your organization or agency can transform your ability to deliver impactful services that better the lives of those you serve.
Successfully measure and improve your outcomes with Bonterra Impact Management.




