Nonprofit case management guide: strategies, challenges, and tips

Nonprofit organizations dedicate themselves to making a positive impact, and effective nonprofit case management is crucial to achieving their goals. However, maximizing impact with limited resources requires strategic planning, dedication to your mission, and the right tools.
This guide explores key nonprofit case management challenges and provides actionable strategies to overcome them, helping your organization better serve its clients and achieve its goals.
What is case management?
Case management is a collaborative process that involves assessing, planning, and coordinating services to meet clients’ health and human services needs. In essence, case management for nonprofit organizations is about building a supportive relationship with individuals and empowering them to create a better future for themselves.
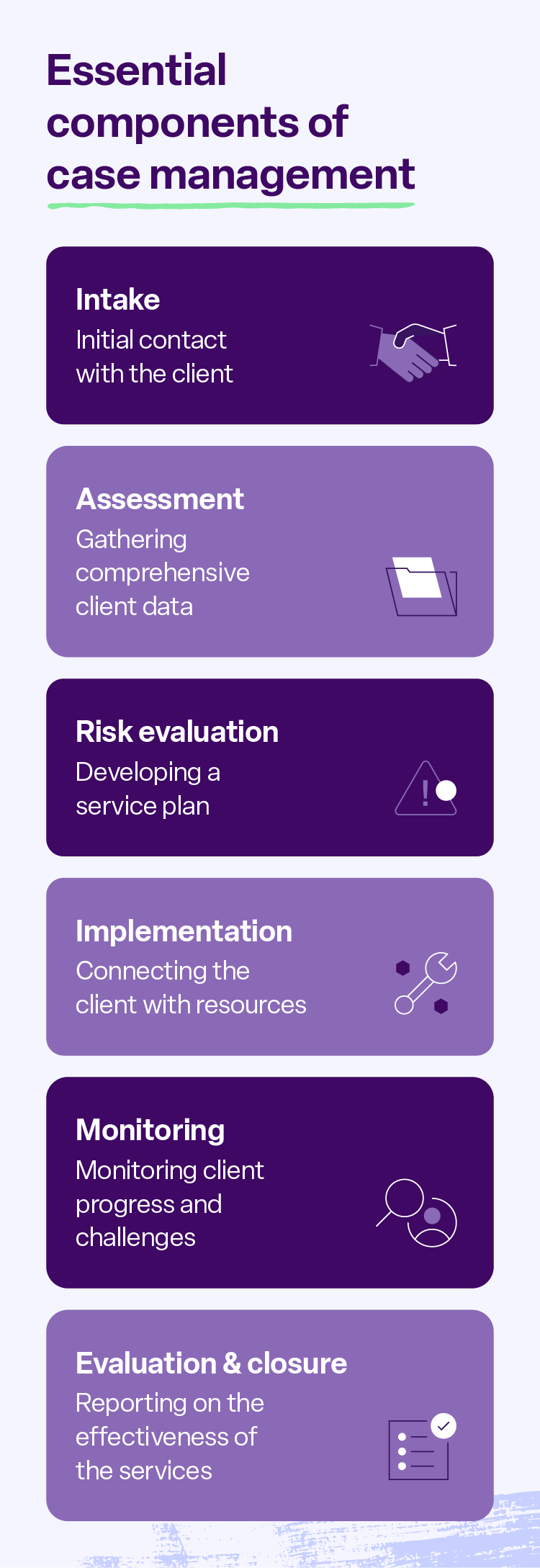
How does the case management process work?
The case management process typically begins with an initial assessment to understand the client’s situation, needs, and goals. From there, a plan is developed collaboratively, outlining specific steps and resources needed to achieve those goals.
Here’s a breakdown of how case management strategies work:
- Intake and screening: Initial contact with the client, gathering basic data and information, and determining service eligibility.
- Assessment: Gathering more comprehensive information about the client’s needs, strengths, challenges, and goals.
- Risk evaluation: Developing a service plan in collaboration with the client, outlining specific goals and interventions.
- Implementation: Connecting the client with resources and services, such as housing, healthcare, employment assistance, or counseling.
- Monitoring: Regularly checking in with the client to monitor their progress, address any challenges, and make adjustments.
- Evaluation: Assessing and reporting on the services’ effectiveness and the client’s progress toward their goals.
- Closure: Ending the case management relationship when the client’s goals have been met or when services are no longer needed.
4 types of case management models
When it comes to case management strategies, there’s no one-size-fits-all approach. Understanding the four main case management models can help you choose the best approach for your team and the people you serve.
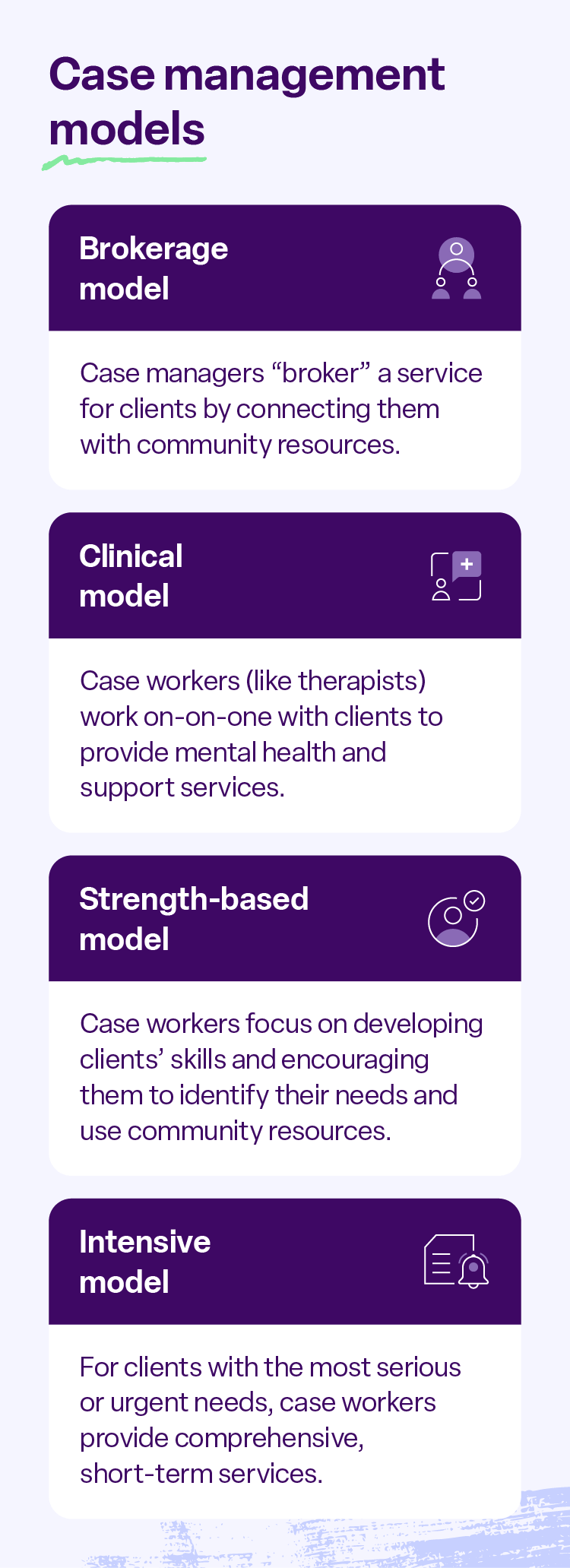
Brokerage case management
Brokerage case management is all about connecting clients with the right resources. Think of the case manager as a “broker” whose main job is identifying the client’s needs and connecting them to the appropriate resources.
The case manager plays a key role in making referrals to the right places and then monitoring things to make sure the client is actually getting the support they need.
Clinical case management
Clinical case management takes a more hands-on approach. Unlike brokerage case management, where the case manager primarily connects clients with external resources, in the clinical model, the case manager often provides the services themselves.
In this model, the focus is on providing direct services and therapeutic interventions to clients. This can include things like individual therapy, group counseling, crisis intervention, and medication management.
Strengths-based case management
Strengths-based case management flips the script on traditional approaches by focusing on what clients can do rather than what they can’t.
Case managers collaborate with clients, acting more as partners than directors. They encourage clients to identify their needs and goals, explore their strengths and support networks, and develop action plans that leverage these resources.
Intensive case management
Intensive case management is designed for individuals with the most complex and challenging needs, often those facing serious and persistent mental illness, homelessness, or substance abuse disorders.
Intensive case managers play a crucial role in crisis intervention, advocacy, and assistance with daily living skills. They may also provide direct services, such as medication monitoring or support with accessing healthcare.
Common case management challenges
Many organizations struggle with limited resources, high caseloads, and complex client needs. Adopting a case management solution can help you overcome these challenges and provide the best possible support to your clients and community.
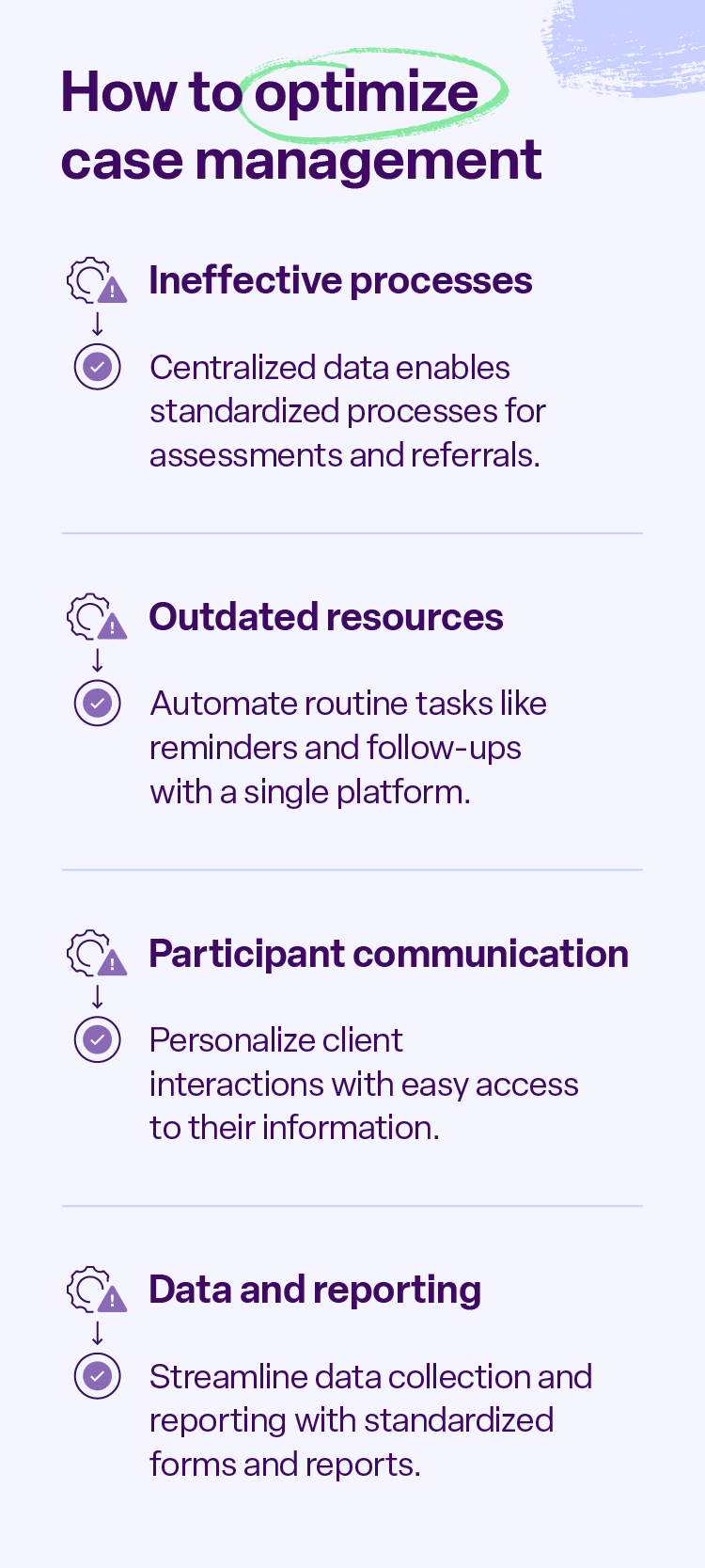
Ineffective processes
When workflows are poorly defined, rely on outdated manual methods, or lack clear communication channels, case managers find themselves bogged down in unnecessary administrative work.
These inefficiencies not only reduce the time available for direct client interaction but also increase the risk of errors in service delivery. Additionally, ineffective processes often lead to data silos, where crucial client information is scattered across different platforms, making it difficult for case managers to get a comprehensive view.
Outdated resources
Many case management organizations struggle with outdated resources, particularly when it comes to technology. Instead of a single streamlined system, case managers spend excessive time on manual processes, such as paper-based record-keeping, manual data entry, and hand-generated reports.
This often translates into heavy workloads for staff due to the limitations of inadequate tools.
Participant communication
Effective communication plans are the cornerstone of successful case management, yet they can often be challenging.
Strained communication can make it difficult to build rapport, accurately assess needs, develop effective service plans, and monitor progress. This can lead to missed appointments and, ultimately, hinder the participant’s ability to achieve their goals.
Data and reporting
One of the biggest challenges nonprofits face is the inability to quickly and easily access the data they need. Compiling reports and analyzing trends becomes time-consuming when information is scattered across multiple systems, stored in outdated formats like spreadsheets, or simply not collected systematically.
This lack of accessible data has significant consequences, especially when it comes to securing funding. Grant proposals and funding applications often require detailed data on program outcomes, client demographics, and service utilization.
Without the ability to efficiently generate these reports, organizations can struggle to demonstrate their impact and make a compelling case for funding.
Tips for improving nonprofit case management
While executing a case management strategy can be challenging, the right software can help streamline processes to maximize your impact.
Investing in a nonprofit case management system — a single platform for all your reporting and data management needs — can centralize client information, automate administrative tasks, facilitate communication, and generate insightful reports.
When utilizing a centralized data system, follow these case management organization tips to improve efficiency:
- Personalize communication: With all client data at your fingertips in one platform, you can easily tailor messages to build rapport. Leverage built-in tools like direct messaging, connect portals, and collaboration features for secure information sharing.
- Systemize processes: Having data in one central system allows you to create standardized procedures for common tasks like intake, assessments, and referrals. This helps reduce errors and makes it quicker and easier for staff to follow protocols.
- Automate workflows: Leverage the power of a single platform to set up automated triggers for routine actions such as sending appointment reminders, generating follow-up emails, or flagging cases that require immediate attention. This reduces manual work, ensures timely follow-up, and frees up case managers to focus on other client needs.
- Utilize templates: Use standardized forms and report templates to simplify data intake and reporting. This facilitates consistent data collection, reduces data entry errors, and allows for quick report generation for internal tracking or external reporting needs.
Expand your impact with case management software
Fulfill your mission with support where you need it most. A nonprofit case management system can help transform your organization’s ability to serve its clients and achieve its mission.
Streamline program processes, improve communication, and centralize data with the right collaborative case management system.
FAQ
What is case management in nonprofit organizations?
Nonprofit case management is the process of assessing client needs, developing individualized service plans, coordinating resources and support, and monitoring progress toward achieving specific goals.
What are the four types of case management?
The four main types of case management are:
- Brokerage: Connecting clients with existing resources.
- Clinical: Providing direct therapeutic services.
- Strengths-based: Focusing on client strengths and abilities.
- Intensive: Providing high-intensity support for complex needs.
What’s the best case management software for nonprofits?
The “best” case management software depends on a nonprofit’s specific needs, but a comprehensive solution offers one platform for all your reporting and management needs, centralizing client data, automating tasks, and streamlining workflows for maximum impact.
Work with Bonterra



