ESG vs. CSR: Key strategies and benefits for companies

What’s the difference between CSR vs. ESG?
The Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) and Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) movements have gained significant momentum as a growing number of corporations and their investors recognize the importance of taking a holistic approach to sustainability. These movements represent an opportunity for corporations to adopt more ethical practices, but there can be a lot of confusion comparing ESG vs. CSR and how they differ.
In this guide, we’ll answer some common questions surrounding these initiatives, clarify the purpose of each, and explore how they can impact your corporate philanthropy efforts.
What is corporate social responsibility (CSR)?
CSR is a management practice that encourages employees to contribute to larger environmental and societal goals through philanthropic activities like volunteering and donating to charitable organizations.
CSR started as a concept in Howard Bowen’s 1953 book, Social Responsibilities of the Businessman. In short, Howard suggests that businesses should positively impact society and proposes CSR as a strategy to do so.
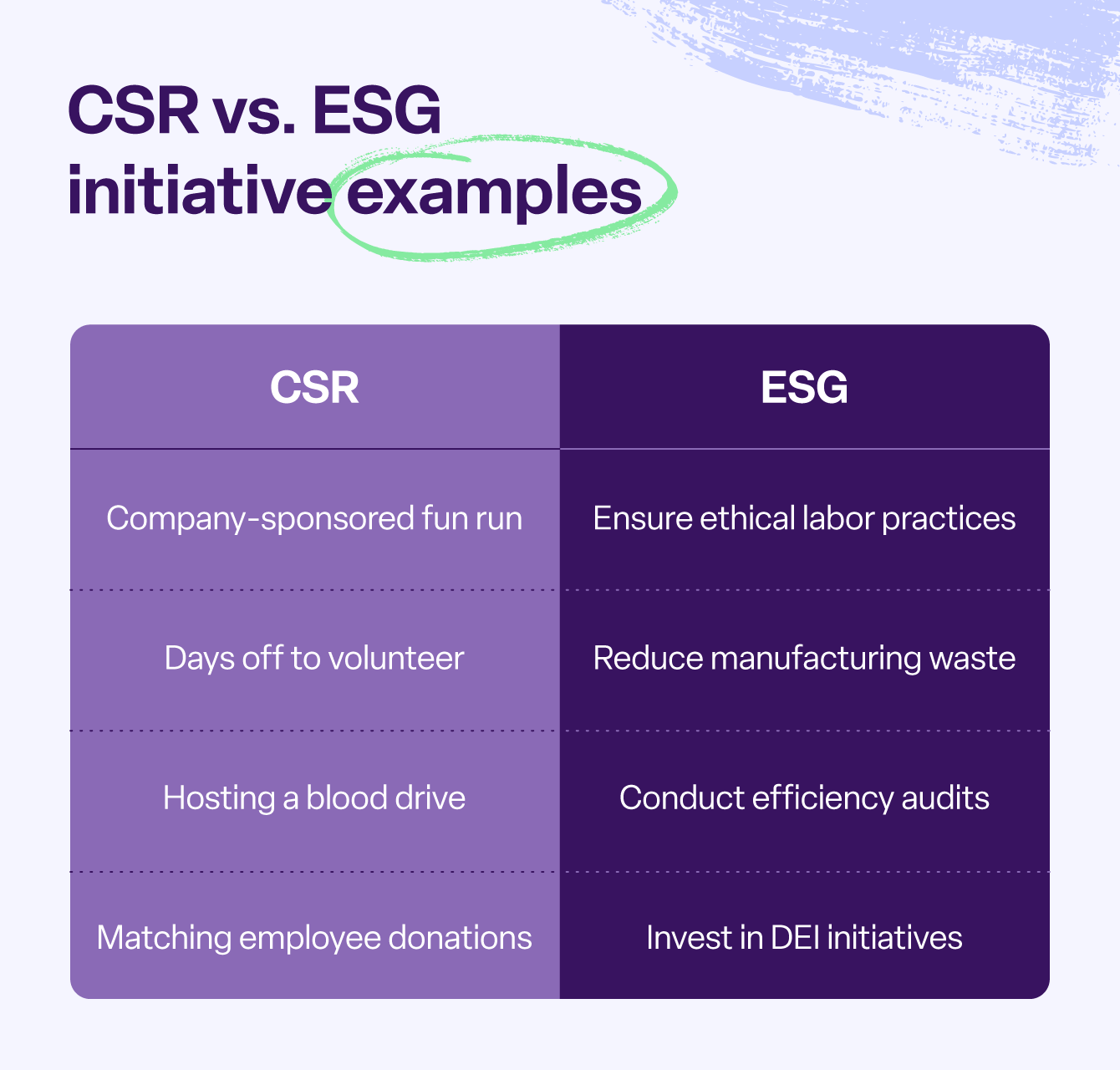
CSR initiatives include actions such as partnering with nonprofit organizations, which provide qualitative positive results on the larger community.
Key CSR elements
There are a few elements and goals that make up the different types of CSR initiatives. Generally, these initiatives target a combination of these elements:
- Environmental: Positive impacts on the environment through initiatives such as reducing resources
- Ethical: Maintaining ethical business practices such as providing a safe working environment and fair wages
- Economic: Prolonged investment in CSR initiatives, such as creating a CSR budget
- Philanthropic: Supporting larger CSR goals through donation matching or volunteer days

What is environmental, social, and governance (ESG)?
The ESG movement is a more comprehensive extension of the CSR movement. It refers to the overall sustainability and social impact of a corporation, focusing on measurable impacts instead of a general drive to do good.
The movement started as a CSR initiative launched by the United Nations but has since grown into a global phenomenon. ESG is defined by various frameworks and benchmarks that measure a business’ moral influence. Essentially, it encourages investors to take a holistic view of success beyond just financial performance. ESG recognizes that a company’s environmental approaches, social initiatives, and governance practices influence long-term success and value creation.
ESG is as valuable to businesses as ever. Investors want to align their portfolios with values that contribute to positive societal outcomes. Companies measure ESG targets using quantitative reporting so investors and shareholders can see the numbers that reveal how these initiatives impact their ROI.
Key ESG elements
Stakeholders participating in the ESG movement account for a range of factors when evaluating a corporation’s impact. These factors and ESG initiative examples include:
- Environmental sustainability: Operating in an environmentally responsible manner, such as minimizing carbon emissions and water usage
- Social impact: Committing to social responsibility through fair labor practices, diversity and inclusion initiatives, and community engagement efforts
- Governance practices: Ensuring equitable internal management and control systems, such as board diversity, executive compensation, and risk management policies
Key differences between CSR vs. ESG
CSR and ESG are similar initiatives — especially because ESG grew from CSR. For a quick overview of the difference between CSR and ESG, you can reference this table before we dive deeper.
| CSR | ESG | |
| Purpose | Improved public relations | Improved internal processes |
| Reporting | Qualitative reporting | Quantitative reporting |
| Implementation | Voluntary and requires active planning | Regimented and tied with compliance |
Purpose
ESG and CSR have similar goals to improve society but different philosophies of how and why businesses need those goals. ESG’s purpose is generally risk management. Whether the risk is depleting resources or mistreating employees, ESG aims to improve those circumstances, which could boost business value.
CSR’s purpose is more about general social responsibility. It advocates that businesses take actions such as donation-matching because it’s the right thing to do — not to mention a good PR move.
Reporting
ESG vs. CSR reporting is very different. ESG has no “global standard” for reporting, so each business measures success differently. Generally, ESG reports are more qualitative, but there’s a lot of potential for change here as the industry works to set standards.
For example, an ESG target might be to reduce single-use plastic in an office. The initiative could include providing water bottles and filtered water for office employees. The company might measure this impact based on how many water bottles employees take from the break room fridge.
In contrast, CSR’s impacts can be more difficult to quantify but they’re typically measured by output vs. outcome. For example, if a CSR initiative aims to improve community outreach, the business might give employees time off to volunteer at a local school.
In this situation, the number of volunteer hours would be the output. To evaluate the outcome, the business might survey teachers and students. A survey can give insight into how the initiative is performing, but it won’t provide definite, measurable metrics.
Implementation
Generally, ESG implementation is very regimented because these initiatives often include following labor laws, providing sufficient benefits, and other required initiatives. However, some companies might go above and beyond with non-essential initiatives like hiring a consultant to explore how they can become an environmentally friendly office.
CSR implementation isn’t a governed process, so it takes active investment from a company to hit CSR targets.
For example, a business isn’t required to partner with nonprofits and drive donations but might do so as a CSR initiative. The business must determine what resources to put into this initiative, who will oversee it, and how they’ll measure the outcome.
The benefits of adopting ESG and CSR
Although there’s no current federal mandate for ESG or CSR in the US, it’s a growing trend among businesses and has become an expectation from investors and the public.
We’ll discuss some basic CSR benefits in detail below.
Brand reputation
Both ESG and CSR initiatives can positively impact a business’s reputation. They convey that a business values more than just revenue and is taking steps to benefit society as a whole. Additionally, investors and stakeholders expect companies to take a proactive approach to environmental and sustainability issues. ESG and CSR initiatives can demonstrate this approach and attract investors.
Competitive advantage
Early ESG and CSR adoption can give a business an advantage over competitors who don’t have these initiatives in practice. Early adoption helps build a positive reputation from the onset of a business and yields greater returns in collective impact, employee engagement, and brand reputation.
Compliance
Although CSR isn’t connected to compliance, ESG has strong ties to it. A defined ESG plan makes it easier to comply with environmental or labor regulations because it lays out what actions a business will take and how it will measure success from the start.
Boost revenue
ESG and CSR considerations can help your company identify and mitigate risks that impact its financial health. In particular, ESG supports compliance with local regulations and reduces the chance of legal issues or fines that can impact businesses’ financial health.
How CSR software helps streamline processes
ESG and CSR have myriad benefits but without the right resources, they can be difficult to start. Managing CSR efforts can take a lot of effort, between planning initiatives, building philanthropic relationships, engaging employees, and measuring output.
Corporate social responsibility software takes some of the pressure off this process with features that can help employees achieve more for their communities:
- Measure employee participation
- Boost employee engagement
- Track donations and volunteer hours
- Connect with nonprofits
- Simplify grant making
- Enable international collaboration
- View impact and regulation compliance via straightforward dashboards

Better manage your corporate social responsibilities with Bonterra
Whether you’re weighing the decision to start ESG vs. CSR initiatives, allow companies to build stronger relationships with stakeholders, enhance their reputation, and help ensure their long-term sustainability in an increasingly complex business environment.
Work with your team to choose the right CSR software to maximize your efforts and align them with your company’s goals and values. Discover how Bonterra is helping to build a more ethical and sustainable future for business.
FAQ
Is CSR the same as ESG?
No, CSR isn’t the same as ESG. CSR initiatives focus on big-picture social efforts like creating volunteer opportunities, and ESG initiatives focus on more internal improvements, such as reducing a business’ energy consumption.
What sets ESG apart from CSR?
CSR focuses on creating larger societal impacts with initiatives rooted outside of a business. ESG considers not only social and environmental factors but also governance issues such as executive compensation, board diversity, and internal controls.
Should you adopt ESG practices?
Whether or not a company should align itself with ESG practices depends entirely on its unique values, priorities, and long-term goals. However, stakeholders and investors are beginning to expect ESG reports, so it’s good to be ahead of the curve.
How do CSR activities support ESG goals?
CSR activities provide practical initiatives that advance ESG objectives. Employee volunteering supports social impact metrics, while corporate recycling programs contribute to environmental targets. These CSR initiatives generate measurable data for ESG reporting, helping companies show concrete progress in their sustainability journey.
Work with Bonterra



